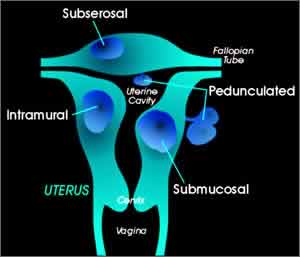
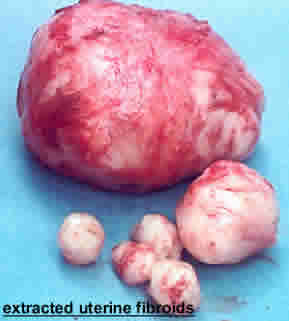
Fibroid is also known as a uterine leiomyomata or “myoma,”. Fibroid is a lump or growth in the uterus that is not cancerous. Fibroids can be as small as a pea to as large as a basketball. Fibroids are usually round and pinkish in color, and they can grow anywhere inside or on the uterus. While some women have only one fibroid, they typically are present in groups of two or more.
About 30% of women older than 30 years have fibroids, and they usually appear between the ages of 35 and 45.
Uterine fibroids are the most common female pelvic tumor, affecting up to 30% of women. Fibroids are non-cancerous tumors that arise from smooth muscle cells within the uterus and can result in symptoms such as pelvic pain, pelvic pressure, urinary frequency, abdominal fullness, infertility and heavy menstrual bleeding. Fibroids can be microscopic and some fibroids may weigh several pounds. While it is unclear what causes fibroids to form, we do know fibroids depend on estrogen to grow and are more common in African-American women.
Treatment options for fibroids vary upon the severity of symptoms, a patient's age and medical history, as well as her desire to maintain fertility. Simple treatment options include monitoring with ultrasound, oral contraceptive pills or hormone injections to control fibroid growth. A myomectomy, or surgical removal of fibroids, can be performed. ysteroscopically, larparoscopically or abdominally. In addition, uterine artery embolization (UAE), performed by an interventional radiologist, is designed to restrict the fibroid's blood supply. The benefit of UAE is avoidance of surgecal removal of fibroids, but long-term results are unknown, as is the affect on future pregnancy.
 Doctors agree that there is no single best approach to fibroid
treatment. There are many treatment options that exist. The best action
to take after discovering fibroids is simply to be aware they are
there. Since fibroids are non-cancerous and if fibroids are small and
are not causing any symptoms, they do not need to be treated.
Doctors agree that there is no single best approach to fibroid
treatment. There are many treatment options that exist. The best action
to take after discovering fibroids is simply to be aware they are
there. Since fibroids are non-cancerous and if fibroids are small and
are not causing any symptoms, they do not need to be treated. 
